*This post may have affiliate links, which means I may receive commissions if you choose to purchase through links I provide (at no extra cost to you). As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. Please read my disclaimer for additional details.
A steady power source is needed for homeschooling and work from home opportunities. The number of users at home has skyrocketed while large three-phase electric units aren’t in service. How do you know the difference between residential and commercial power lines?
What is the difference between single-phase and three-phase electricity?
The main difference between single and three-phase is the number of conductors. Single-phase passes through one conductor while three-phase goes through three. Additionally, three-phase is geared to supply constant power at much higher wattages for industry.
Understanding how electric currents and circuits work can be a daunting task. The combination of wires and voltages are enough to make your head spin.
If you want to feel safe and not lost in the sauce when it comes to electricity, read on—while dangerous, learning about how currents work can be an advantageous experience.

Table of Contents
Single Phase Electricity
Single Phase electricity is the kind that we have in our homes. It powers things like:
- Lighting
- Heating
- Cooling
- Refrigeration
- Appliances
Single-phase wiring is the kind we see stretched along streets in communities. It is used to power the large heating and cooling units that are in most homes.
The power flows in a down and back pattern. For instance, a circuit is formed when the current leaves the source (LIVE), travels to the appliance (DEVICE), back to the neutral wire (NEUTRAL), and into the ground (GROUND). It makes a diagram that looks like this:
LIVE—>DEVICE—>NEUTRAL—>GROUND
The critical thing to remember is that it makes a circle. If there are other places in the circuit, say the wire is leaking electricity to a shower floor; when it comes into contact with a human, it will jump into them.
A severe shock can cause electrocution. There are unique outlets, GFCI outlets, that protect from this, but we will discuss those later.
Single Phase Benefits
Each system will come with its own set of benefits and shortcomings. For single-phase, the pros are:
- An Array of Appliances – Several appliances run off of single-phase power.
- Less Complex – When it comes to working on these yourself, it can be relatively easy.
- More Efficient – These are more efficient when distributing watts up to 1000.
When you see a set of single-phase wiring coming to your house, more than likely, it came from a transformer.
A transformer works to keep the flow constant by offering two separate currents to bounce back and forth.
This back and forth creates 230v of power, which is the standard range for any electrical machines that you might have in your home.
Three Phase Electricity
Three-phase electricity is on the gigantic metal towers that you see while driving in open spaces.
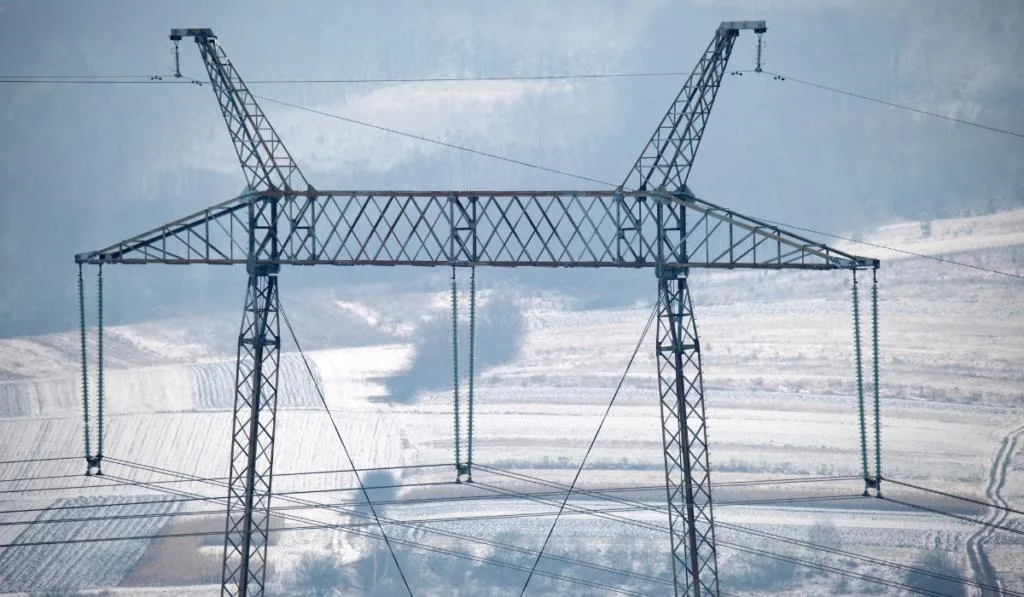

Three-phase is what supplies industry with the massive amount of power that they need to make heavy-duty machines operate.
The energy with three-phase is constant and doesn’t require a transformer. However, when a three-phase begins to shrink down to residential homes, a series of transformers make the power accessible by the households.
Three-phase motors can create a magnetic field during operation. The area can be used to power electric motors and generators.
The steady flow of a three-phase system will allow for much smoother operation of these types of motors. The constant back and forth of a single-phase would make the engine sluggish and run irregularly.
Three Phase Benefits
When it comes to three-phase, the stakes are higher. The benefits that a three-phase system are:
- Phase Current Cancels – The current in a three-phase system cancels the other out. That means you can use a smaller bit of conductor for the ground because of the lack of flow.
- Constant Power – If you have to run an electric engine or motor, you need continuous power. When an electric engine loses power, in a car, for example, the extra components (transmission, etc.) grind to a sudden halt. Causing undue wear on the parts.
- Magnetic Field – The magnetic field that a three-phase electric system works off of means you don’t need a starter. Fewer parts mean fewer things to break down.
GFCI Outlet Function
GFCI stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. It does exactly what it says. If there is a fault in the ground, the area where an electric wire is attached to something that won’t conduct electricity, the outlet will stop functioning.
As was mentioned earlier, GFCI outlets are outlets that cut off when flow moves outside the circle.

For instance, when you get out of the shower, an exposed wire could make the floor and every wet surface a conductor for electricity.
With the GFCI outlet, there is a type of circuit breaker inside, which cuts off flow if there is an imbalance of power.
The standard range on a GFCI outlet is 5 milliamps (source). To provide an example, it takes around 30 milliamps to cause electrocution, which means that these types of outlets can provide a very safe barrier between a mild shock and death.
Types Of GFCI’s
There are three main types of GFCI’s that we see almost every day. They are:
- Portable – This type is most commonly seen on extension cords. It is easy to spot by the long rectangular box close to the female end of the plug. There will be a red and black set of buttons. This is the GFCI.
- Outlet – The place that you see these most often are in the kitchen and bath. If there is a leak in electricity, it could flow into the plate around the outlet. When you touch the outlet, you get to ride the lightning. Again, look for the pair of buttons that will be marked. If the switch is triggered, all you need to do is press the opposite button, and power will be restored.
- Circuit Breaker – If you have a home with an older circuit breaker, this is a type of GFCI. When excess power flows back into it, a switch flips and cuts power to the room. Older window AC units are bad about flipping a circuit breaker. Overloading a power source can be dangerous.
Tamper Resistant And GFCI
It isn’t hard to mix up a tamper-resistant socket and a GFCI. Each has extra buttons that make it stand apart from other conventional outlets. They have the same function, but each has its unique design that protects the user from shocks.
With the tamper resistant outlet, there is a spring-loaded mechanism that will close off the portal to power if a foreign object is stuck inside.
For example, say you have a child who finds a paper clip and jams it in the outlet if it is tamper-proof, a tiny door inside slams and stops the object from traveling too far inside the outlet.
GFCI outlets are made for additional plugins like USB ports. A USB can be mounted side by side with a regular outlet. That’s great because there is always a need for a place to charge a phone.
Inside the GFCI is a circuit breaker of sorts. When a surge of power flow heads back towards the user, it cuts off. A switch would usually be flipped inside the circuit breaker, but with a GFCI, you only need to flip the switch on the face.
Both were invented to protect the user from shock or electrocution. As a rule, construction in most states requires a GFCI be installed in:
- Kitchen
- Bathroom
- Laundry Room
- Pool Deck
The need for the outlets in these areas is higher because, aside from plain water, the added chemicals to bath and kitchen water could increase the conductivity of electricity.
Resources
- https://thewirecutter.com/reviews/best-wall-outlets-with-usb-charging-ports/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/HomeImprovement/comments/3hmrau/gfci_usb_combo_outlet_anybody_know_where_to_find/
- https://www.elprocus.com/difference-between-single-phase-and-three-phase-ac-power-supply/
- https://safeelectricity.org/ground-fault-circuit-interrupters-gfcis/
- https://www.electricaltechnology.org/2015/02/gfci-ground-fault-circuit-interrupter-types-working.html
